Exact Cell Decomposition
Exact Cell Decomposition divides the space into non-overlapping cells. This is commonly done by breaking up the space into triangles and trapezoids, which can be accomplished by adding vertical line segments at every obstacle's vertex.
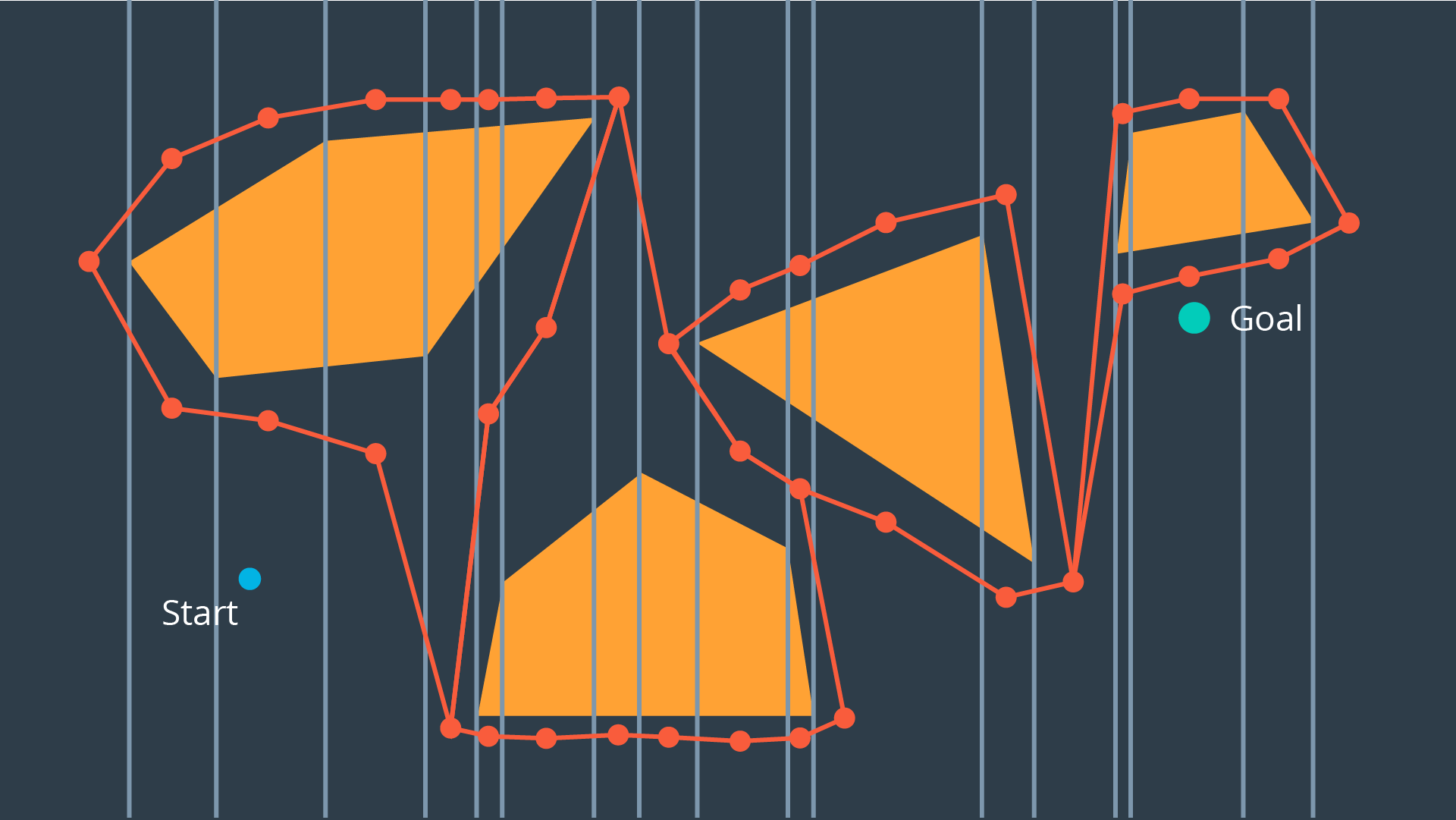
Once a space has been decomposed, the resultant graph can be used to search for the shortest path from start to goal.
Advantages
Exact cell decomposition is elegant because of its precision and completeness. Every cell is either "full, meaning it is completely occupied by an obstacle, or it is "empty", meaning it is free. And the union of all cells exactly represents the configuration space. If a path exists from start to goal, the resultant graph will contain it.
To implement exact cell decomposition, the algorithm must order all obstacle vertices along the x-axis, and then for every vertex determine wheterh a new cell must be created or whether two cells should be merge together. Such an algorithm is called the Plane Sweep Algorithm.
Disadvantages
Exact cell decomposition results in cells of awkward shapes. Collections of uniquely-shaped trapezoids and triangles are more difficult to work with than a regular rectangular grid. This results in an added computational complexity, especially for s with greater number of dimensions.
It is also difficult to compute the decomposition when obstacles are note polygonal, but of an irregular shape.